Enhancing Workplace Safety Through : Energy Control Program-Lockout/Tagout
Enhancing Workplace Safety Through : Energy Control Program-Lockout/Tagout
In the realm of workplace safety, few protocols are as crucial as those governing energy control. The Energy Control Program, often referred to as Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), stands as a cornerstone of occupational safety, designed to safeguard workers from hazardous energy sources. With the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Standard 1910.147 setting the guidelines, adherence to these procedures is not just recommended, but legally mandated for many industries. The procedures for lockout/ tagout are seen by many as complex but can be effectively learned today through occupational safety and health training.
What is the Energy Control Program?
At its core, the Energy Control Program is a systematic method aimed at preventing accidental machine start-up or release of stored energy during servicing or maintenance activities. This is particularly vital in industries where machinery or equipment utilize various forms of energy, such as electrical, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, chemical, or thermal.Safety courses that is carefully crafted for use in online safety training platforms can provide employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to manage this systematic process.
Understanding Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)
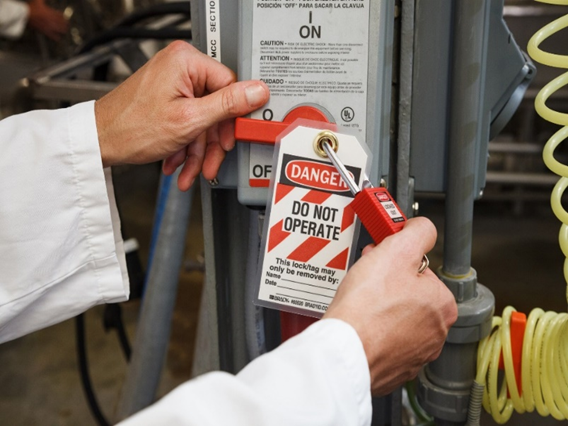
Safety and health training are paramount for employees and organizations in the control of hazardous energy. Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) is a vital safety procedure within the broader Energy Control Program, designed to protect workers from hazardous energy sources during equipment maintenance or servicing. This protocol involves the physical isolation of energy-isolating devices, such as switches or valves, through locking mechanisms to prevent accidental activation. Additionally, a visible tag is affixed to the locked device, providing crucial information about the status of the equipment and identifying the individual responsible for the lockout. LOTO procedures are essential for ensuring the safety of workers by effectively preventing unexpected machine start-ups or the release of stored energy, thereby reducing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries.
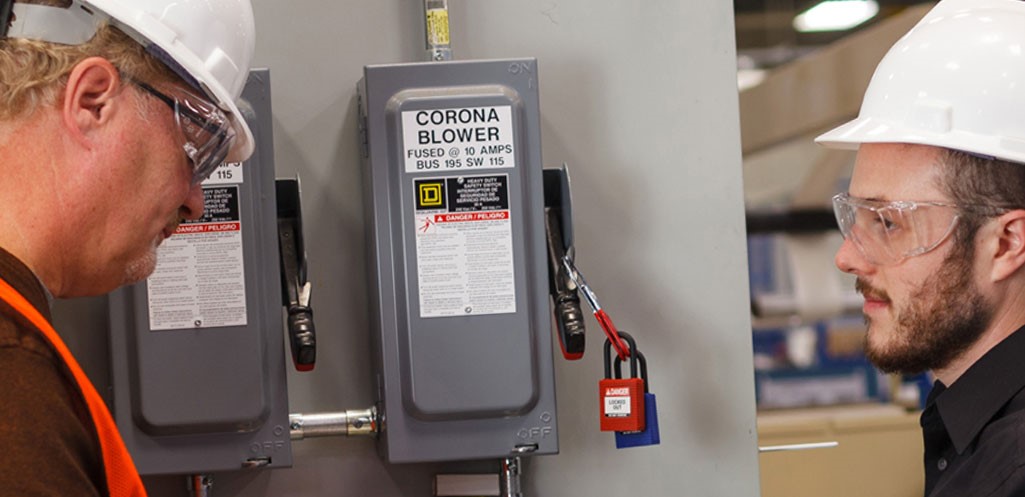

The Importance of OSHA Standard 1910.147
The significance of OSHA Standard 1910.147 cannot be overstated in fostering workplace safety across industries. This standard establishes clear guidelines and requirements for the control of hazardous energy, serving as a cornerstone for the development and implementation of effective Energy Control Programs. By mandating the adoption of energy control procedures, employee safety and health training, and regular inspections. OSHA 1910.147 aims to mitigate the risks associated with hazardous energy sources and safeguard the well-being of workers. Compliance with this standard not only helps organizations adhere to legal obligations but also demonstrates a commitment to prioritizing employee safety and reducing the incidence of workplace accidents and injuries. OSHA Standard 1910.147 serves as a crucial framework for promoting a culture of safety within workplaces, ultimately contributing to the protection of lives and the preservation of health in the workforce.
OSHA Standard : Control of Hazardous Energy (Lockout/Tagout)
https://www.osha.gov/laws-regs/regulations/standardnumber/1910/1910.147
Key Components of OSHA Standard 1910.147
Energy Control Procedures: Employers must develop, document, and implement specific procedures for the control of hazardous energy. These procedures should encompass all forms of energy sources and provide clear instructions for safely de-energizing equipment.
Employee Training and Awareness: OSHA mandates comprehensive safety and health training programs to familiarize employees with energy control procedures and the importance of LOTO. Employees must understand how to properly apply and remove lockout/tagout devices and recognize the risks associated with hazardous energy.
Periodic Inspections and Reviews: Regular inspection procedures which can be learned through online safety training are necessary to ensure the effectiveness of energy control procedures and identify any potential deficiencies. Employers must review and update their Energy Control Program as needed to reflect changes in equipment or processes.
Equipment-Specific Procedures: To meet OSHA compliance each piece of equipment requires maintenance and servicing and must have its own energy control procedures. These procedures should address the unique characteristics and hazards associated with the equipment, ensuring that workers can safely isolate energy sources.
Implementing an Effective Energy Control Program
Establishing a robust Energy Control Program requires a collaborative effort between employers and employees. Here are some essential steps to ensure its effectiveness:
Risk Assessment: Identify all sources of hazardous energy within the workplace and assess the associated risks. Understanding the potential hazards is crucial for developing appropriate control measures. The risk assessment process is vital, and employees can gain the skills of performing this critical task through on the job work experience and by participating insafety and health training.
Written Procedures: Document clear and concise energy control procedures for each piece of equipment. These procedures should include detailed steps for isolating energy sources, applying lockout/tagout devices, and verifying the effectiveness of the control measures.
Employee Training: This involves providing comprehensive occupational safety and health training to all employees involved in maintenance or servicing activities. Whenonline safety training is used it covers the proper use of lockout/tagout devices, recognition of hazardous energy sources, and procedures for responding to emergencies.
Communication and Collaboration: Foster open communication between employees, supervisors, and management regarding energy control procedures. Encourage collaboration to identify potential improvements and address any concerns raised by workers.
Regular Audits and Reviews: Conduct periodic audits of the Energy Control Program to ensure compliance with OSHA standards and identify areas for improvement. Solicit feedback from employees and incorporate their input into program revisions.
Missouri Department of Labor and Industrial Relations: Sample Energy Control Program
https://labor.mo.gov/dls/workplace-safety/energy-control-LOTO-program
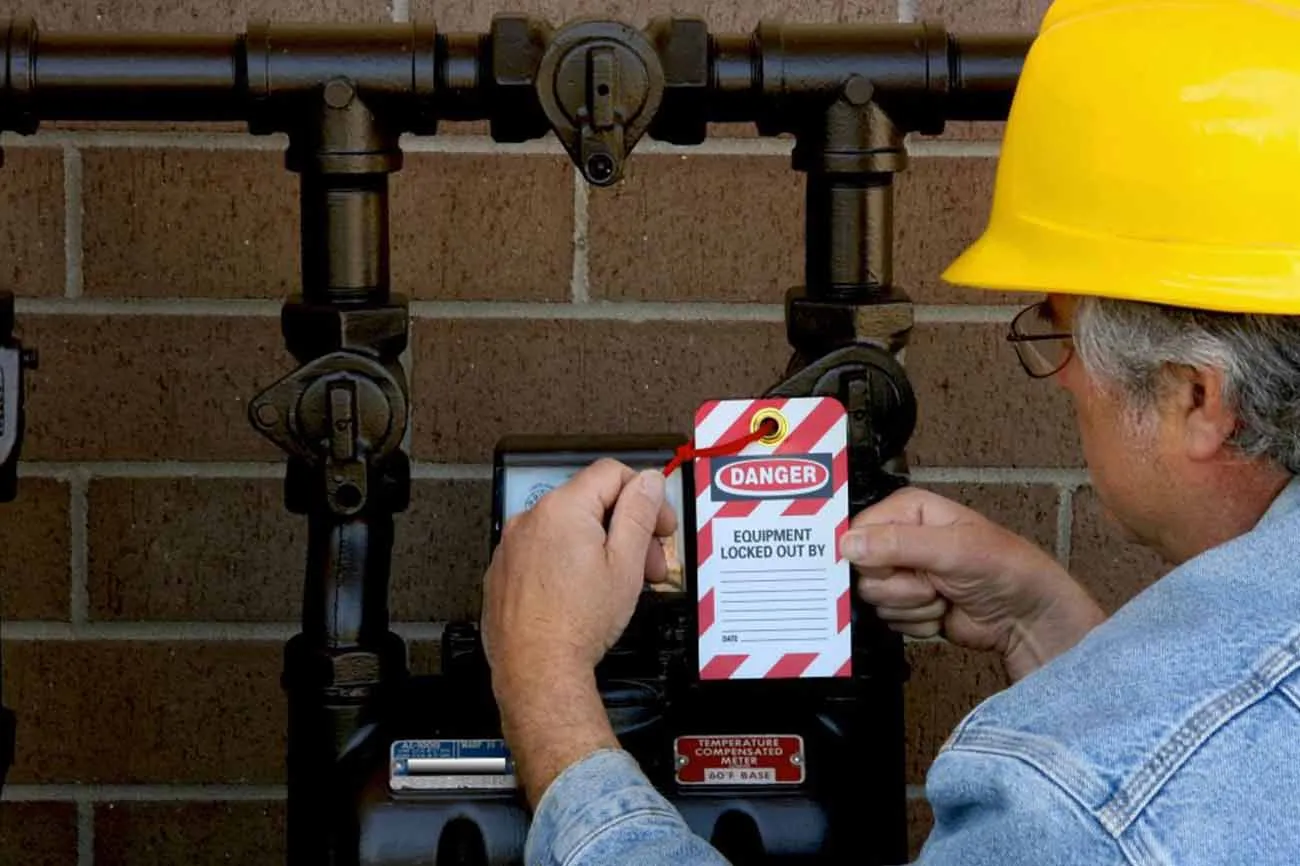

Steps in The Lockout Tagout Procedure
Implementing a thorough lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedure is critical to ensuring the safety of employees during maintenance or servicing of equipment. Training of these procedures are of great importance and should be reinforced through well-structured safety and health training. The procedure typically involves several key steps:
Notify Affected Employees: Before initiating any maintenance or servicing activities, it is essential to inform all affected employees about the planned lockout/tagout procedure. Clear communication ensures that everyone is aware of the equipment that will be taken out of service and the associated safety measures.
Identify Procedure and Hazards: Prior to starting the lockout/tagout process, identify the specific energy control procedures for the equipment being serviced. Conduct a thorough assessment to identify potential hazards associated with the machinery and develop a comprehensive plan to mitigate these risks.
Shut Down Equipment: Once the affected employees are notified and the hazards are identified, shut down the equipment using the appropriate procedures outlined in the manufacturer’s guidelines or standard operating procedures. Ensure that all machine functions are stopped safely before proceeding to the next step.
Isolate Machine from Energy Source: After shutting down the equipment, take measures to isolate it from all energy sources. This may involve turning off power sources, closing valves, or blocking flow paths to prevent the inadvertent release of hazardous energy.
Apply Lockout/Tagout Devices: Affix lockout/tagout devices to energy-isolating devices, such as switches, valves, or breakers, to physically prevent them from being operated. Locks and tags should be durable, standardized, and clearly labeled to indicate the reason for the lockout and the identity of the authorized personnel.
Check Stored Energy: Before proceeding further, it is essential to verify that all potentially hazardous stored energy sources have been safely released or dissipated. This may involve bleeding hydraulic or pneumatic systems, draining capacitors, or relieving tension in springs.
Verify Isolation: Once lockout/tagout devices are applied and stored energy is released, verify that the equipment is effectively isolated from all energy sources. This step ensures that there is no residual energy that could pose a risk to workers performing maintenance or servicing tasks.
Tryout and Test: Before commencing with maintenance or repairs, conduct a tryout or test to ensure that the equipment is properly isolated and in a safe condition. This may involve attempting to start the machine to verify that it remains inoperative.
Bring Equipment Back Online: Once maintenance or servicing activities are completed and all personnel are clear of the area, remove lockout/tagout devices and restore energy to the equipment in accordance with established procedures. Take care to follow proper start-up procedures to prevent any unexpected hazards.

OSHA compliance can be met by adhering to these steps. Meticulously following these steps can help organizations mitigate the risk of accidents and injuries associated with energy control procedures and ensure the safety of their workforce during maintenance or servicing operations.
Lockout Tagout Procedures
https://www.bradyid.com/resources/lockout-tagout-procedures
Lockout/Tagout Procedures: 10 Steps to Follow
https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/steps-of-lockout-tagout
Benefits of Compliance with Energy Control Programs
Adhering to energy control procedures and LOTO protocols offers numerous benefits to both employers and employees:
Reduced Risk of Accidents and Injuries:
Proper implementation of LOTO procedures significantly reduces the risk of accidental machine start-up or release of stored energy, minimizing the potential for workplace injuries and fatalities.
Legal Compliance: Compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.147 ensures that employers meet their legal obligations to provide a safe working environment for employees. Failure to comply can result in costly fines and penalties.
Enhanced Productivity: While LOTO procedures may temporarily interrupt workflow for maintenance activities, the long-term benefits include improved equipment reliability, fewer unplanned downtime incidents, and increased productivity.
Improved Employee Morale: By prioritizing safety through the implementation of energy control programs, employers demonstrate their commitment to protecting the well-being of their workforce, which can boost employee morale and job satisfaction.
Safety and Health Training in Energy Control Program
Safety and health training play a pivotal role in the effective implementation of an Energy Control Program, particularly concerning lockout/tagout procedures. Comprehensive safety courses provide employees with the knowledge and skills necessary to understand the hazards associated with hazardous energy sources and the proper techniques for safely isolating them. Online safety training offers a convenient and accessible platform for disseminating essential information to workers, allowing them to learn at their own pace and on their own schedule. By incorporating OSHA compliance standards into online safety and health training modules, organizations can ensure that employees receive up-to-date and relevant instruction on energy control protocols. Moreover, online safety and health training enables employers to track employee progress, verify completion of required safetycourses, and maintain detailed records to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Furthermore, safety and health training foster a culture of safety within the workplace, empowering employees to take ownership of their safety and that of their colleagues. Through interactive safety courses, workers gain a deeper understanding of the importance of adhering to lockout/tagout procedures and the potential consequences of failing to do so. By emphasizing the significance of compliance with OSHA regulations and best practices in energy control, online safety training instills a sense of responsibility and accountability among employees. Ultimately, investing in safety and health training not only enhances workplace safety and reduces the risk of accidents and injuries but also contributes to overall organizational success by promoting a culture of safety excellence.

Conclusion
The Energy Control Program, governed by OSHA Standard 1910.147, plays a pivotal role in safeguarding workers from the dangers of hazardous energy sources in the workplace. By implementing effective lockout/tagout procedures and adhering to energy control protocols, employers can mitigate the risk of accidents, ensure regulatory compliance, and foster a culture of safety within their organizations. Investing in comprehensive training, regular inspections, and continuous improvement efforts is essential for maintaining the integrity of the Energy Control Program and protecting the health and safety of all employees.
Author: Dr. O’Neil G. Blake, Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Safety Result Professionals
MS., MBA., MSc., BSc, CSP., ASP., CSHM., CSMP., MRSA.
Date: 04-16-2024